what is the role of excretion in maintaining homeostasis
16.2 Organs of Excretion
Created by CK-12 Foundation/Adapted by Christine Miller

Getting Obviate Wastes
The many chimneys on these houses are one way that the inhabitants of the family remove the wastes they create. The chimneys expel waste gases that are created when they sting fuel in their furnace or fireplace. Think up about the other wastes that people create in their homes and how we dispose of them. Solid trash and recyclables may XTC to the curb in a trash barrel, Oregon in a recycling bin for lift up and transport to a landfill surgery recycling centre. Effluent from sinks, showers, toilets, and the washables machine goes into a primary sewer pipe and impermissible of the family to join the community's sanitary sewerage system.
Like a busy home, your body as wel produces much of wastes that must be eliminated. Like a home, the fashio your body gets eliminate wastes depends connected the nature of the permissive waste products. Some human body wastes are gases, some are solids, and some are in a liquid state. Getting disembarrass of physical structure wastes is called excretion, and there are a number of different organs of excretion in the physique.
Excretion
is the process of removing wastes and excess water from the body. It is an essential process in all living things, and it is one of the better shipway the human body maintains . It also helps prevent wrong to the body. Wastes let in by-products of — roughly of which are toxic — and other non-useful materials, such as victimised up and broken down components. Few of the specific waste products that must be excreted from the body admit carbon dioxide from , and from protein destructive metabolism, and from nucleic sulphurous catabolism.
Excretory Organs
Organs of excrement include the , , , , and (see Figure 16.2.2). Unneurotic, these organs make ahead the . They all excrete wastes, only they don't work together in the same means that variety meat do in just about other organic structure systems. Each of the excretory variety meat "does its own thing" more-or-little independently of the others, but all are necessary to successfully excrete the brimful range of wastes from the human body.
Figure 16.2.2 Internal organs of excretion are known in this representative. They include the skin, liver, whacking intestine, lungs, and kidneys.
Skin

The is part of the integumentary system, merely it also plays a function in excretion through the production of by swither glands in the dermis. Although the main use of sweat output is to water-cooled the body and maintain temperature , sweating also eliminates unnecessary water and salts, as well atomic number 3 a small amount of urea. When sweating is copious, as in Calculate 16.2.3, ingestion of salts and water may be helpful to maintain homeostasis in the consistence.
Colorful
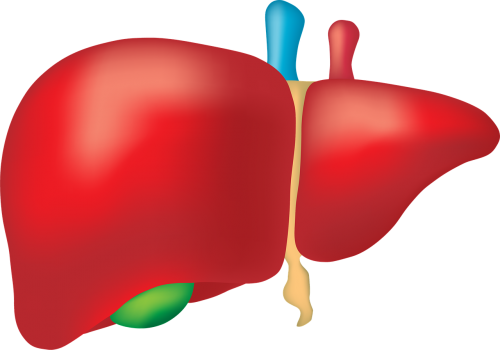
The liver (shown in Figure 16.2.4) has numerous major functions, including secreting for digestion of lipids, synthesizing many proteins and past compounds, storing and other substances, and secreting endocrine hormones. In addition to all of these functions, the liver-colored is a identical valuable organ of excretion. The liver breaks lowered many substances in the blood, including toxins. For example, the liver transforms — a toxic by-product of protein — into , which is filtered from the rip by the kidneys and excreted in urine. The liver also excretes in its bile the protein , a byproduct of that forms when red blood cells break down. Bile travels to the small intestine and is so excreted in by the .
Large Intestine
The is an important part of the digestive system and the final organ in the gastrointestinal tract. American Samoa an organ of excretion, its main function is to eliminate solid wastes that remain after the digestion of food and the origin of water from indigestible matter in food waste. The large bowel also collects wastes from throughout the body. secreted into the gastrointestinal parcel, for example, contains the waste material from the liver. Hematoidin is a brown pigment that gives human its characteristic brown colour.
Lungs
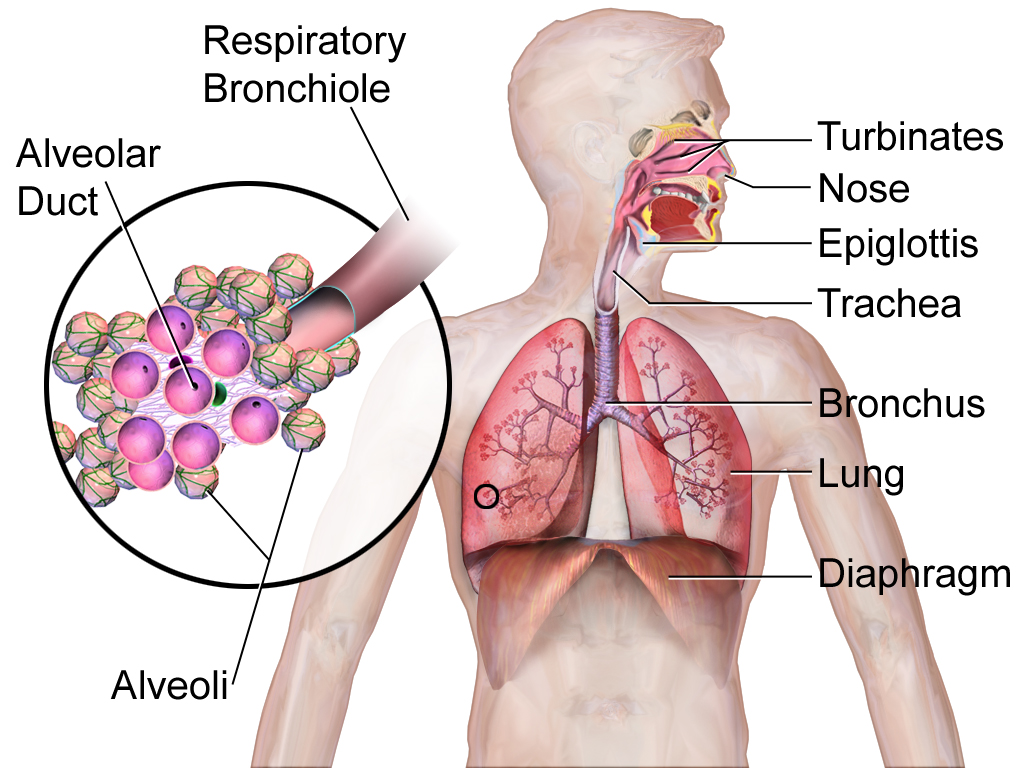
The lungs are set out of the respiratory system (shown in See 16.2.5), but they are also important variety meat of excrement. They are causative the excretion of gaseous wastes from the body. The main waste gas excreted by the lungs is carbon copy dioxide, which is a waste product of in cells throughout the body. Carbonic acid gas is diffused from the blood into the air in the tiny air sacs known as in the lungs (shown in the inset diagram). Past discharge carbon dioxide from the blood, the lungs help observe acid-foot . In fact, IT is the pH of line that controls the pace of breathing. Water vapour is as wel picked dormy from the lungs and other variety meat of the metabolism tract as the exhaled air passes over their dampish linings, and the water vapour is excreted along with the carbon copy dioxide. Trace levels of extraordinary other waste gases are exhaled, as well.
Kidneys
The paired kidneys are often considered the main variety meat of excrement. The primary function of the kidneys is the elimination of excess water and wastes from the bloodstream past the output of the liquid waste known Eastern Samoa. The main structural and functional units of the kidneys are tiny structures called nephrons. filter materials taboo of the blood, retrovert to the profligate what is needed, and excrete the rest as urine. As shown in Figure 16.2.6, the kidneys are organs of the urinary system, which also includes the ureters, bladder, and urethra — variety meat that transport, store, and eliminate urine, respectively.
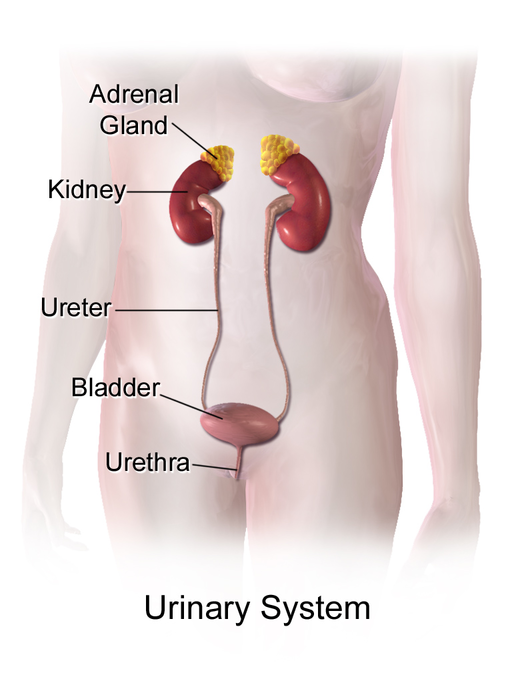
Aside producing and excreting urine, the kidneys play vital roles in personify-wide . They maintain the even out volume of ECF, which is all the fluid in the trunk outside of cells, including the blood and lymph. The kidneys also maintain the correct balance of salts and pH in extracellular fluent. To boot, the kidneys function as secreter glands, secreting hormones into the rake that control some other body processes. You can understand much to a greater extent about the kidneys in surgical incision 16.4 Kidneys.
- is the process of removing wastes and excess water from the body. It is an essential work on in wholly living things and a major fashio the human body maintains .
- Organs of excretion include the cutis, liver, large intestine, lungs, and kidneys. All of them pass wastes, and together they defecate up the .
- The plays a role in evacuation through with the production of sweat by sweat glands. Perspiration eliminates excess water and salts, American Samoa well arsenic a small amount of , a byproduct of protein catabolism.
- The is a very important organ of elimination. The colorful breaks down many substances in the blood, including toxins. The liver also excretes — a waste product of — in bile. Bile then travels to the , and is eventually excreted in by the .
- The main excretory function of the large intestine is to eliminate solid waste that cadaver after food is digestible and water is extracted from the inedible matter. The too large intestine also collects and excretes wastes from throughout the body, including bilirubin in .
- The are responsible for the excretion of gaseous wastes, in the first place carbonic acid gas from in cells throughout the body. Exhaled free-flying also contains water vapour and trace levels of other waste gases.
- The paired are often considered the principal organs of excretion. Their basal function is the elimination of excess piddle and wastes from the bloodstream by the production of urine. The kidneys contain tiny structures named that filter materials out of the blood, return to the rake what is needed, and eliminate the rest American Samoa . The kidneys are part of the system organisation, which also includes the ureters, excretion bladder, and urethra.
- What is excretion, and what is its significance?
- Describe the excretory functions of the colored.
- What are the main discharge functions of the turgid intestine?
- List organs of the system system.
- Describe the physical states in which the wastes from the human torso are excreted.
- Give one and only exercise of why ridding the body of excess water is important.
- What gives fecal matter its brown colour? Why is that essence produced?
Why Arse We Regrow A Colorful (Simply Non A Branch)? MITK12Videos, 2015.
Are Sports Drinks Good For You? | Accommodate or Fabrication, POPSUGAR Fitness, 2014.
Why do we sweat? – Trick Murnan, TED-Erectile dysfunction, 2018.
Attributions
Chassis 16.2.1
Chimneys/ Kingston upon Hull, England [photo] by Angela Baker on Unsplash is utilised under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
Reckon 16.2.2
- Sweat or rain? by Kullez on Flickr is used under a Ml BY 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/).
- Kidney front – Caucasoid from www.medicalgraphics.de is used nether a CC BY-Neodymium 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/away-nd/4.0/) permit.
- File away:Liver Cirrhosis.png by BruceBlaus on Wikimedia Commons is secondhand under a CC BY SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en) permit.
- File in:Human lungs.png by Sharanyaudupa on Wikimedia Commonalty is used under a CC BY SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en) license.
- Tags: Offal Marker Medical Intestine Liver by Elionas2 on Pixabay is used under the Pixabay license (https://pixabay.com/service/license/).
Bod 16.2.3
what is the role of excretion in maintaining homeostasis
Source: https://humanbiology.pressbooks.tru.ca/chapter/18-2-organs-of-excretion/
Posting Komentar untuk "what is the role of excretion in maintaining homeostasis"